Our strategy encompasses a holistic approach to sustainability, where every decision and action is guided by a commitment to transparency and responsible operations.
On this page, you can learn how:
- A circular approach helps us minimise our environmental impact
- Our pioneering use of bioplastic material reduces our plastic footprint
- We are tackling the end-of-product-life challenge with recycling programs
- A growing evidence database enables you to participate in and verify our actions
See also, how Ambu works with environmental, social and governance (ESG) issues
Building circular practices into our product life cycle
The goal is clear: To minimise the environmental impact of our products and packaging as much as possible through a circular approach.
Our Circular Design Guide provides us with a methodology for incorporating circular thinking in all our processes.
Ambu's commitment to reducing our environmental footprint extends throughout the life cycle of our products. From raw material extraction to disposal after use, we recognize the environmental impact of our solutions and are dedicated to minimising it at every stage.
Improve raw materials
Material innovation: Material, such as bioplastics, helps us reduce our reliance on fossil-based materials and instead use plastic material with a lower carbon footprint.
Healthy substances: Reducing the use of materials of concern, such as PVC, to facilitate safe recycling of our products.
Design to maintain high value
Adopt a circular design approach: In order to maintain the maximum possible value of product material, we employ a modular approach. This makes it possible to recover valuable raw materials for recycling or repurposing at end of product life.
Reduce manufacturing waste
Reduce and recirculate materials, energy and water from manufacturing by-products and waste to make more from less via manufacturing cascades.
Rethink packaging & logistics
Decrease the amount of packaging material via design innovations.
Use more sustainable packaging material, such as bioplastics.
Rethink the product’s journey from supplier to customers and beyond end of life, for example, by shifting to electric vehicles and taking back or recycling products close to their end-of-life location.
Extend product life cycle
Take-back and recycling pilots and partnerships in key regional markets.
Data driven sustainability for product development
Collect and share data to make fact-based decisions and maintain transparency towards customers.

Improve raw materials
Material innovation: Material, such as bioplastics, helps us reduce our reliance on fossil-based materials and instead use plastic material with a lower carbon footprint.
Healthy substances: Reducing the use of materials of concern, such as PVC, to facilitate safe recycling of our products.
Design to maintain high value
Adopt a circular design approach: In order to maintain the maximum possible value of product material, we employ a modular approach. This makes it possible to recover valuable raw materials for recycling or repurposing at end of product life.
Reduce manufacturing waste
Reduce and recirculate materials, energy and water from manufacturing by-products and waste to make more from less via manufacturing cascades.
Rethink packaging & logistics
Decrease the amount of packaging material via design innovations.
Use more sustainable packaging material, such as bioplastics.
Rethink the product’s journey from supplier to customers and beyond end of life, for example, by shifting to electric vehicles and taking back or recycling products close to their end-of-life location.
Extend product life cycle
Take-back and recycling pilots and partnerships in key regional markets.
Data driven sustainability for product development
Collect and share data to make fact-based decisions and maintain transparency towards customers.
Taking leaps towards a more sustainable future
As a first mover in sustainability innovation for our area, we set ambitious goals for minimising our environmental footprint.
- Bioplastics in all currently marketed endoscope handles by end of 2024
- 95% of new products released after 2025 to be PVC-free
- Bioplastics in all currently marketed endoscope handles by end of 2024
- 95% of new products released after 2025 to be PVC-free
- Take-back and recycling offering in focus markets by 2025
- Long term goal is to design for recycling
Ambu’s pioneering use of bioplastic material
Plastic is considered a safe, flexible material for medical devices, which is gentle on the human anatomy. However, as conventional plastics are often derived from fossil-based and non-renewable resources, we continuously explore ways to reduce our reliance on fossil-based materials and reduce the carbon footprint of our endoscopes and other medical devices and packaging.
Our use of bioplastics in our endoscopy solutions and bioplastics in our laryngeal mask cuff protectors are tangible examples of this.
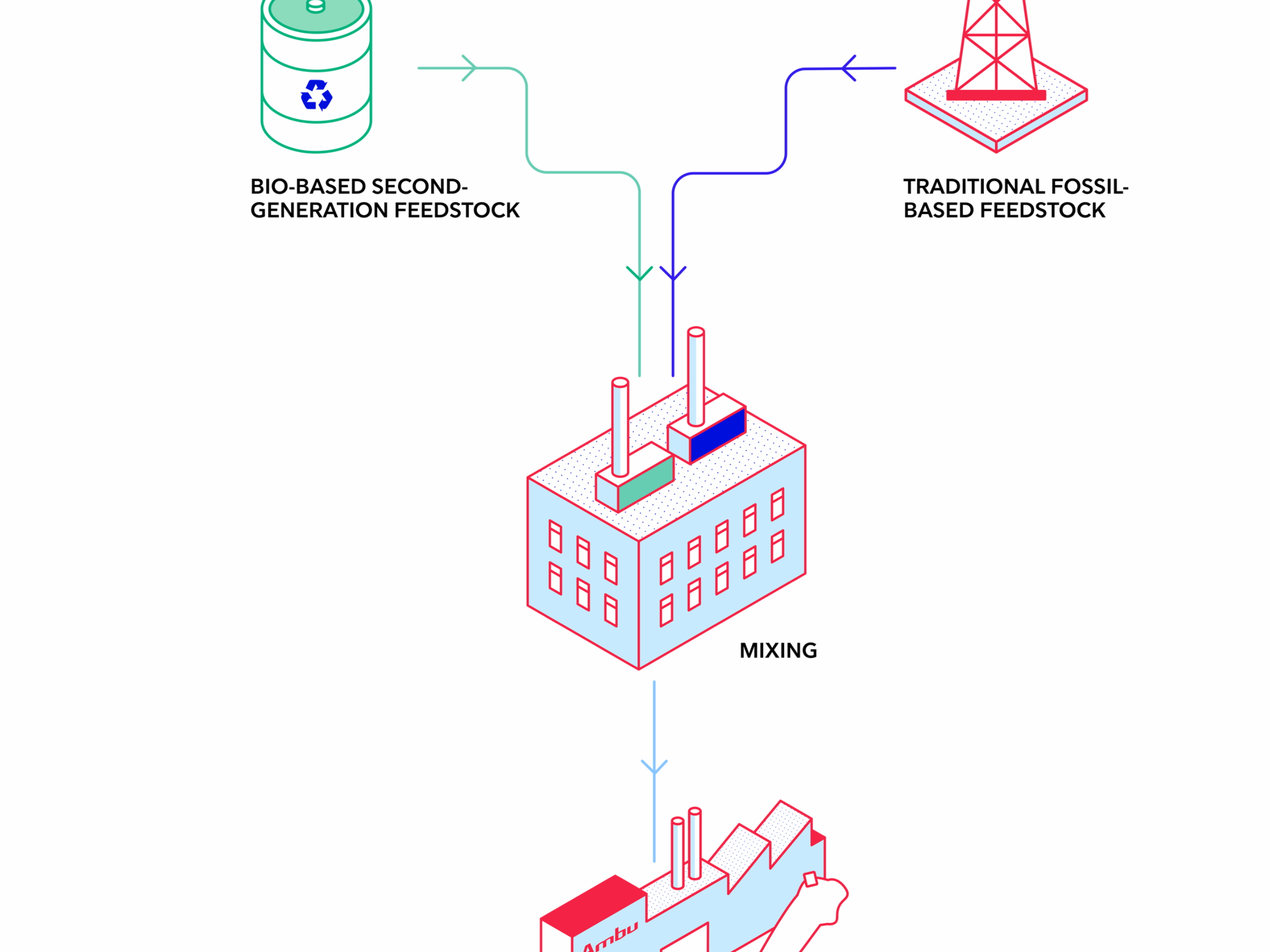
How bioplastics are made
TRADITIONAL FOSSIL-BASED FEEDSTOCK
Crude oil is extracted from the ground and cleaned in a refinery to produce plastics.
BIO-BASED SECOND-GENERATION FEEDSTOCK
Food & agricultural waste, such as cooking oil (that doesn’t compete with food and agriculture production) is gathered, and cleaned in the refinery to produce plastics.
MIXING
For some bioplastics (like bio-ABS) fossil-based feedstock (crude oil) and bio-based second-generation feedstock (used cooking oil) are mixed together in a 50/50 ratio* during the production of the bioplastics.
AMBU PRODUCTS WITH BIOPLASTICS
Bioplastic material is as strong and durable as fossil-based plastic. The performance of our products with bioplastic are the same, but now with a lower carbon footprint.
Bioplastic material contains plant-based carbon stored during the plant growing process, which contributes to a lower carbon footrpint when compared to traditional plastics.
* Certified under a mass-balance scheme
5 facts about our use of bioplastics
Our use of second-generation bio-based feedstock used in the bioplastic material in our products:
- Represents one tangible example of action in our mission to reduce our use of fossil-based plastics and decrease our products’ carbon footprint.
- Does not harm biodiversity: Made from by-products and waste, like used cooking oil, that do not compete with food and agriculture production.
- Enables use of material with a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to traditional fossil-based plastics.*
- Will be expanded upon: We will increase the amount of bioplastics in our products and packaging and investigate alternative materials with an even lower carbon footprint.
- Opens new possibilities to recycle waste into new products. The material is not biodegradable ‒ a deliberate choice on our part to ensure that our products are durable and can be be recycled or repurposed at their end of life.
*The bioplastic material (in this case bio-ABS) used in our endoscope handle emits 70% less carbon than traditional fossil-based ABS plastic (based on cradle-to-gate LCA from manufacturer). Note that this reduction refers to the ABS plastic in the handle and not the full endoscope.
Recycling Program
Tackling the end of life challenge
When it comes to handling medically contaminated plastics, traditional recycling methods present a unique hurdle. However, we are committed to overcoming these obstacles through take-back programs, innovative technology and strategic partnerships.
Initiatives include transforming discarded endoscopes into new materials via recycling to extend their life cycle and reduce waste.
Scaling up our offerings
We have set the ambitious target to expand our recycling offerings in all our focus markets in 2025. Our ongoing pilot projects will inform the development of scalable recycling solutions. We believe that this, in turn, will contribute to a more circular healthcare industry where products can be recycled and given a new life.
Currently, we're piloting recycling programs in Germany and the UK, with plans to scale up these initiatives and expand to more markets.
If you want to get involved, you can sign up for our newsletter to hear about the latest partnership and pilot project opportunities.
Data driven approach
A data-driven approach
At Ambu, our focus on transparency enables you to follow along in our sustainability journey. It is one part of a broader strategy that makes sustainability an integral part of our organization.
This strategy encompasses a holistic, verifiable approach to sustainability. Every action and decision is guided by the principles and key performance indicators outlined in our Circular Design Guide. The guide’s data-driven methodology empowers us to:
- Iterate requirements driven by environmental concerns, customer preferences, and regulatory mandates
- Pinpoint the most impactful initiatives, including emerging alternatives with lower carbon footprints
- Make informed decisions with regard to our sustainability ambitions
- Keep our stakeholders informed about the true sustainability performance of our products and business
- Investigate the implications of the cleaning process for reusable devices, which includes harsh chemicals, large amounts of hot water, energy and single-use equipment
A growing evidence database
This data-driven approach has resulted in a growing evidence database of rigorous carbon footprint analyses, Life Cycle Assessments (LCAs), and independent peer-reviewed studies comparing the environmental impact of single-use and reusable flexible endoscopes.
Life cycle assessments
We actively collaborate with specialists to conduct life cycle assessments, enhancing transparency and understanding of our products' environmental performance.
In 2023, we conducted a systematic review of articles quantifying the environmental impact of endoscopy within our areas of operation. It also provided valuable insights into the relative impact of single-use versus reusable endoscopes.
Carbon footprint analyses
Internally, we've established an eco-baseline comprising over 150 products, representing approximately 70% of our sold volume. Through simplified carbon footprint screenings and circularity assessments, we gain insights into the performance of our product families.
Comparative studies
While further research is needed, some independent peer-reviewed life cycle studies have concluded that the impact of single-use endoscopes is equal to or less than that of reusable endoscopes. Learn more
See also:
Environment, Social and Governance: Find information about our ESG priorities, performance and governance structure.
Net zero strategy: Learn about our strategy, validated targets and collaborative approach to achieve net zero emissions by 2045.
Single-use vs. reusable endoscopes: Get an overview of the facts and considerations regarding the impact of single-use endoscopes and how they compare with reusable.

